Student Projects
VM495

Study of Influence of Residual Stress on Simply Supported Beam
Team Members: Feng Yubo, Fan Yixing, Ma Xucheng, Yang Jiaxin, Zhang Zeyu
Project Video
Team Members
Team Members:
Feng Yubo, Fan Yixing, Ma Xucheng, Yang Jiaxin, Zhang Zeyu
Project Description
Introduction
Simply supported beams loaded at the center such as spring-leaf suspensions are common in industrial field. To increase the life of these beams, one way is by introducing compressive residual stresses on the side of the beam that is normally loaded in tension as is shown in figure 1, which will lower the peak tensile stress. This experiment is designed to study the stress-reducing impact of residual stress in simply supported beam.
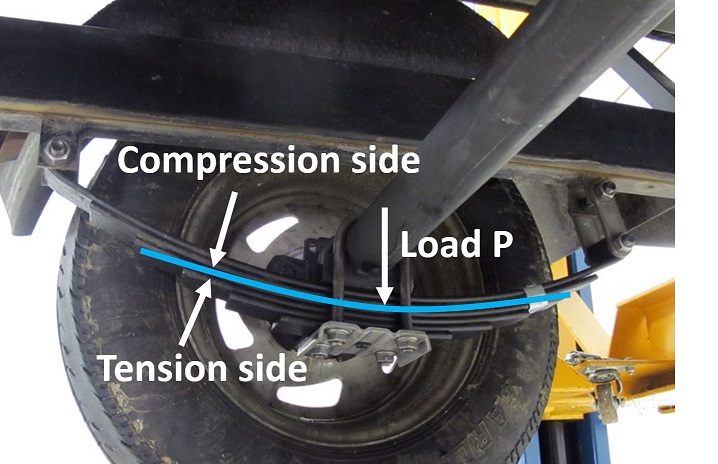
Figure 1. Spring-leaf Suspension System. [1]
Theory
The relationship of surface strain (𝜀_𝑠) and load (P) is:
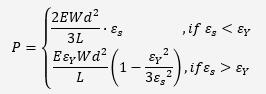
where E is young’s modulus and 𝜀_𝑌 is yield strain. The dimension of the 6061-T6 aluminum W*d*L is shown in figure 2. Figure 3 is the theoretical surface strain-load curve in our case.
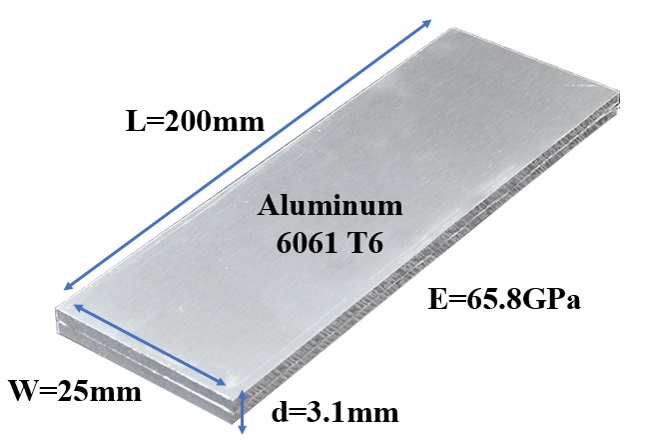
Figure 2. Dimension of Aluminum Beam
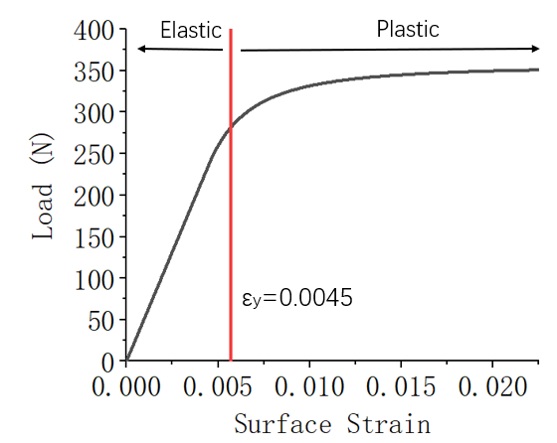
Figure 3. Theoretical Surface Strain-Load Relationship
Experimental
MTS machine is used to
- Perform tensile test → stress-strain curve of 6061-T6 aluminum
- Apply bending load from 0N to 330N → video of bending process recorded by a smart phone camera
Digital image correlation method and MATLAB ncorr tool are used to
- Analyze the pictures from the video → Strain–load curves
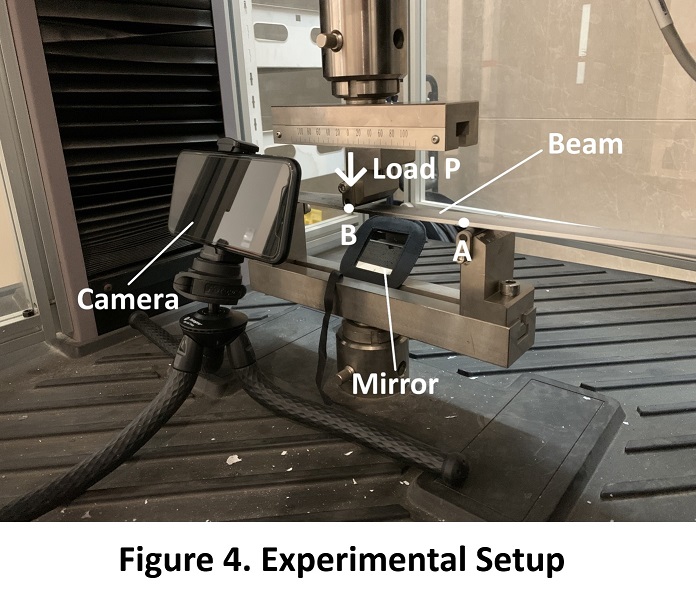
Figure 4. Experimental Setup
Results
We measure the surface strain of the beam while the load increases from 0 to 330N. The surface strain we get through DIC method is shown in figure 5. The surface strain-load curve is shown in figure 6.

Figure 5. Surface Strain from DIC method
Then, we apply a load increasing from 0 to 150N to the plastically deformed beam to obtain the stress-load curve. Figure 7 shows the stress-load curve for the original beam and the deformed beam.
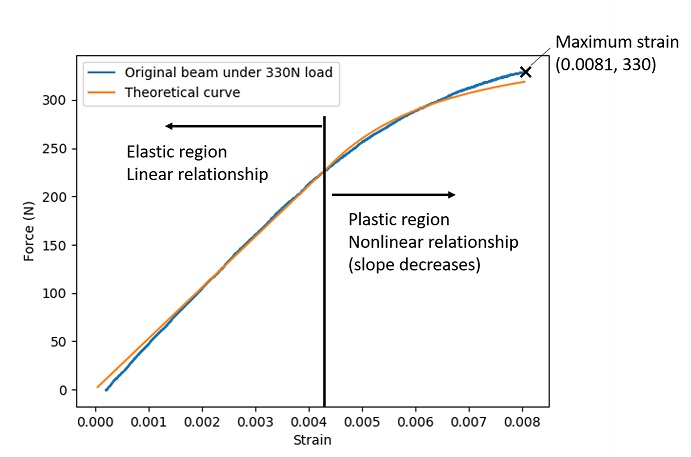
Figure 6. Strain-load Curve
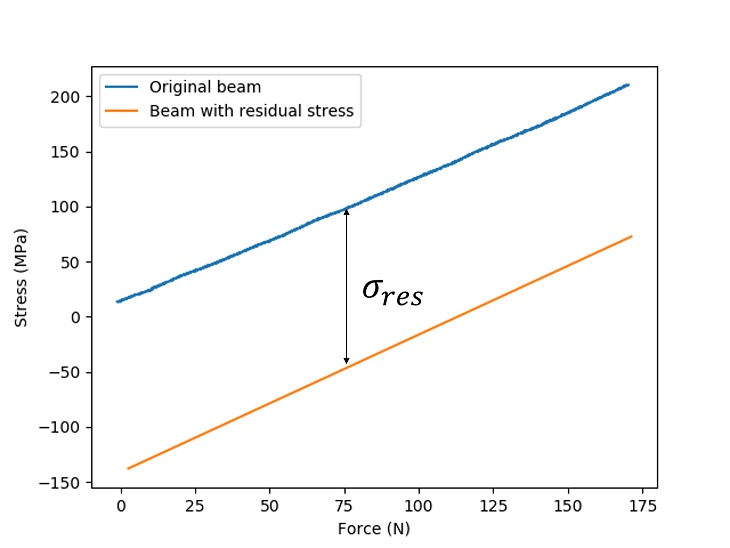
Figure 7. Stress Comparison for Original Beam and Deformed Beam with Residual Stress
Conclusions
Although the maximum stress does not necessarily occur on the surface of the beam, with theoretical analysis, we find that deformed beam with residual stress has smaller stress than the original beam under large loads. The optimal residual stress can be produced by selecting proper pre-load based on the range of the load when the beam is under use.
Acknowledgments
Instructor: Prof. C. P. Chen, Prof. Teh, Kwee-Yan.
Lab assistant: Chen Tianhua
Reference
[1] ] Etrailer. 2020. TRAILER LEAF SPRING SUSPENSION. [online] Available at:
